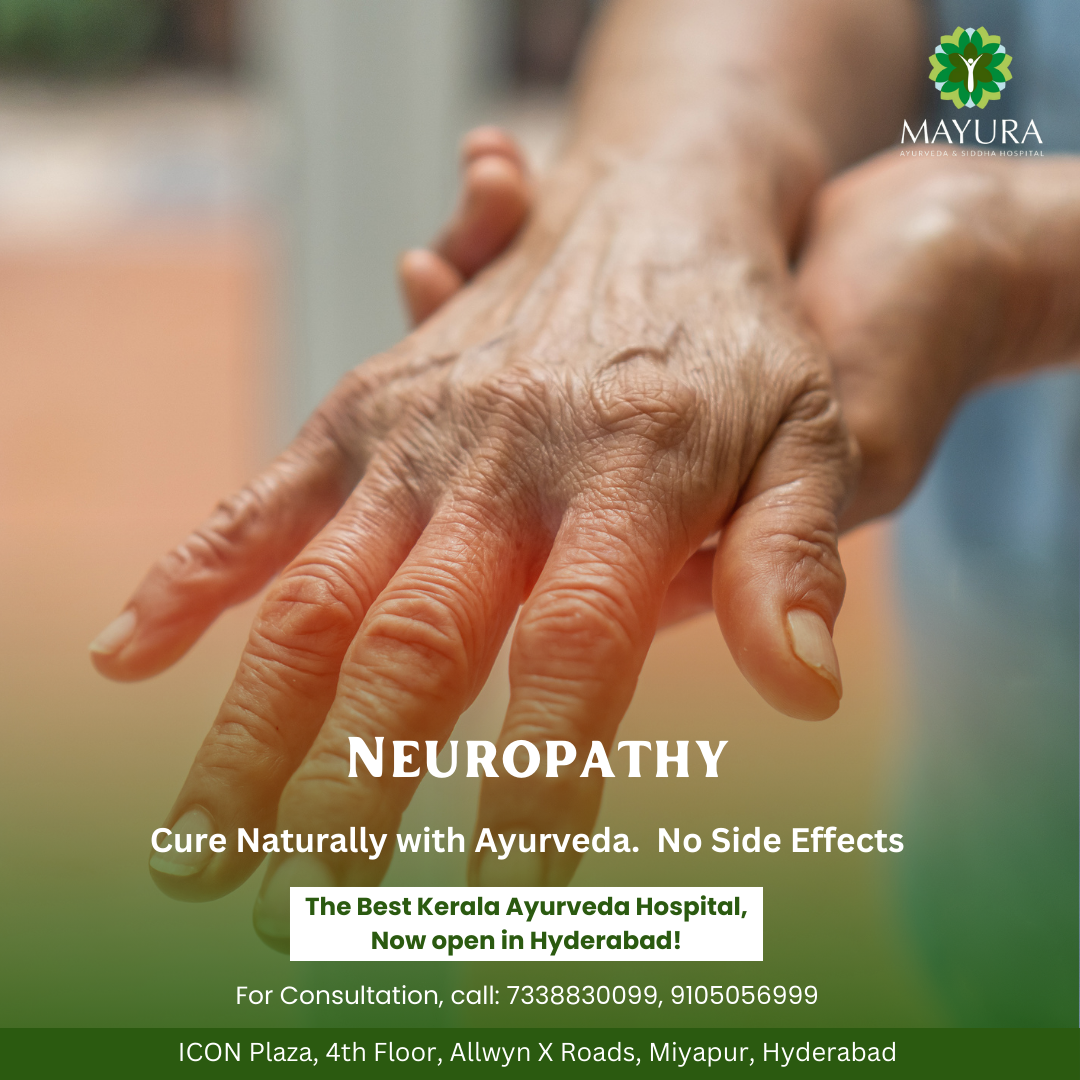
Neuropathy, a complex condition affecting the peripheral nerves, can significantly impact one’s quality of life. As we delve into the intricacies of neuropathy, it becomes essential to comprehend its causes, recognize its symptoms, and explore the diverse treatment options available.
Understanding Neuropathy:
Neuropathy refers to damage or dysfunction of the peripheral nerves, which transmit signals between the central nervous system and the rest of the body. These nerves play a crucial role in controlling various bodily functions, such as muscle movement, sensation, and organ function. When damaged, they can lead to a range of symptoms and complications.
Causes of Neuropathy:
Neuropathy can arise from various causes, making it a diverse and challenging condition to manage. Some common causes include:
1. Diabetes: Elevated blood sugar levels can damage nerves over time, leading to diabetic neuropathy.
2. Trauma and Injury: Physical injuries, accidents, or trauma can result in nerve damage, contributing to neuropathic conditions.
3. Infections: Certain infections, such as Lyme disease, shingles, or HIV, can affect the nervous system and trigger neuropathy.
4. Toxins and Medications: Exposure to certain toxins or the prolonged use of specific medications can lead to nerve damage.
5. Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus can cause the immune system to attack the nerves, resulting in neuropathy.
6. Genetic Factors: In some cases, neuropathy may have a genetic component, making certain individuals more predisposed to developing the condition
Symptoms of Neuropathy:
The symptoms of neuropathy can vary widely depending on the type and severity of nerve damage. Common symptoms include:
1. Tingling and Numbness: A sensation of tingling or numbness, often starting in the hands or feet.
2. Sharp or Burning Pain: Individuals with neuropathy may experience sharp, shooting pain or a burning sensation.
3. Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the muscles, particularly in the affected areas.
4. Coordination Issues: Neuropathy can affect coordination and balance, leading to an increased risk of falls.
5. Sensitivity to Touch: Some individuals may experience heightened sensitivity to touch or temperature changes.
Treatment Options:
Managing neuropathy involves addressing the underlying cause, relieving symptoms, and preventing further nerve damage. Treatment options include:
1. Medications: Pain relievers, anti-seizure medications, and antidepressants may be prescribed to manage symptoms.
2. Physical Therapy: Exercises and physical therapy can improve muscle strength, flexibility, and coordination.
3. Lifestyle Modifications: Controlling underlying conditions, such as diabetes, and making lifestyle changes can help manage neuropathic symptoms.
4. Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture, biofeedback, and certain supplements may provide relief for some individuals.
5. Nerve Stimulation: In some cases, nerve stimulation techniques, such as transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), may be beneficial.
Conclusion:
Understanding neuropathy is crucial for early detection and effective management. By exploring its causes, recognizing symptoms, and exploring various treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps toward improving their quality of life. If you suspect neuropathy or experience symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan.